Introduction to IPA 国际音标简介
1. What is IPA?
IPA stands for the International Phonetic Alphabet. It is designed to give each sound that a human speaking a particular language can produce with a unique symbol. Each symbol represents the place (where in the mouth or throat) and the manner (how the parts of the mouth move and how the breath is used) of producing the sound.
2. The usefulness of IPA in learning Englishi pronunciaition
English spelling system can be very misleading as a reference for pronunciation. The letter "a" in "about, cat, fall, father, make, watch" is pronounced differently. IPA can reflect this difference clearly:
about/  ba ba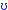 t/ cat/k t/ cat/k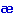 t/ fall/f t/ fall/f :l/ father/f :l/ father/f : :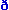  / make/me / make/me k/ watch/w k/ watch/w  / /
According to some theories, learning can be mroe efficient if both the eye and the ear are used. Hearing a sound and seeing its representation in IPA make memorization easier.
IPA is widely used in English dictionaries to transcribe the preferred pronunciation of English words. It is by learning IPA that we can know how to pronounce the phonetic transcriptions in an English dictionary accurately.
3. The DJ(Daniel Jones) System used in OUP dictionaries
In developing his own phonetic system, Daniel Jones, a British phoneticain selected those symbols from IPA that could most accurately represent the pronunciation of British English.
4. Long Vowels, Short Vowels and Diphthongs
The symbol /:/ represents longer duration in pronunciation and is found in long vowels such as /i:/, / :/, / :/, / :/, /u:/, / :/, /u:/, / :/. By contrast, / :/. By contrast, / /, /e/, / /, /e/, / /, / /, /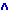 /, / /, / /, / /, /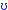 /, / /, / / are called short vowels. Vowels that are made up of tow separate sounds are called diphthongs, such as /e / are called short vowels. Vowels that are made up of tow separate sounds are called diphthongs, such as /e /, /a /, /a /, / /, /  /, / /, / 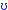 /, /a /, /a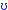 /, / /, /  /, /e /, /e / and / / and /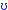  /. They begin with a vowel sound and end with a glide. In pronouncing diphthongs, we move from one vocalic position to another. /. They begin with a vowel sound and end with a glide. In pronouncing diphthongs, we move from one vocalic position to another.
5. How to pronounce (r)
In words such as far /f :(r)/, the symbol (r) indicates that British pronunciation will have /r/ only if a vowel sound follows directly at the beginning of the next word, as in far away /f :(r)/, the symbol (r) indicates that British pronunciation will have /r/ only if a vowel sound follows directly at the beginning of the next word, as in far away /f :(r) :(r)  we we /; otherwise the /r/ is omitted. For American English, all the /r/ sounds should be pronounced. /; otherwise the /r/ is omitted. For American English, all the /r/ sounds should be pronounced.
6. Syllabic Consonants /l/ and /n/
Usaully, a syllable contains a vowel. However, /l/, /n/ sometimes functions as syllables by themselves, without any accompanying vowel, as in bottle / b b tl/ and button / tl/ and button / b b tn/. tn/.
7. The sounds represented by Weak Vowels /i/ and /u/
The sounds represented by /i:/ and / / must always be made different, as in heat /hi:/ compared with hit /h / must always be made different, as in heat /hi:/ compared with hit /h t/. The symbol /i/ represents a vowel that can be sounded as either /i:/ or / t/. The symbol /i/ represents a vowel that can be sounded as either /i:/ or / /, or as a sound which is a compromise between them. In a word such as happy / /, or as a sound which is a compromise between them. In a word such as happy / h h pi/, younger speakers use a quality more like /i:/, but short in duration. pi/, younger speakers use a quality more like /i:/, but short in duration.
In the same way, the two vowels represented by /u:/ and /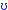 / msut be kept distinct but /u/ represents a weak vowel that varies between them. If /u/ is followed directly by a consonant sound, it can also be pronounced as / / msut be kept distinct but /u/ represents a weak vowel that varies between them. If /u/ is followed directly by a consonant sound, it can also be pronounced as / /. So stimulate can be / /. So stimulate can be / st st mjule mjule t/ or / t/ or / st st mj mj le le t/. t/.
8. Primary Stress and Secondary Stress
Words with more than one syllable must have a main stress/ /, as in butter / /, as in butter / b b t t /, calendar / /, calendar / k k l l nd nd /. Longer words may have a secondary stress / /. Longer words may have a secondary stress / / before the main stress as in academic / / before the main stress as in academic /  k k  dem dem k/, independence / k/, independence /  nd nd  pend pend ns/. ns/.
1. 什么是国际音标?
IPA 就是国际音标(International Phonetic Alphabet) 的缩写,主要是将人类所说的某种语音中可以发出的每个声音,都赋与一个独特的符号。每个符号都代表发音的位置(在口腔或喉咙的哪个部位)及方法(口腔的哪些部位如何移动,以及如何发声)。
2. 国际音标对学习英语发音的帮助
英语的拼法系统很可能成为发音的误导指标。例如字母 a 在 about, cat, fall, father, make, watch 中的发音都不同,而国际音标能够清楚反映其中的差异。
about/  ba ba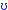 t/ cat/k t/ cat/k t/ fall/f t/ fall/f :l/ father/f :l/ father/f : :  / make/me / make/me k/ watch/w k/ watch/w  / /
根据某些理论,一般人若同时使用眼睛和耳朵,可以学得更快更准。同时看到符号和听到声音更有助于记忆。
国际音标在英语词典中广泛使用,以标注英语单词的发音。藉着学习国际音标,就能知道怎样准确地发出英语词典中标注的语音。
3. 琼斯语音系统
英国语音学家丹尼尔·琼斯(Daniel Jones) 在建立自己的语音系统时,由国际音标中选出最能准确代表英式英语发音的符号。
4. 长元音、短元音及双元音
符号 /:/ 代表发音的时间较长,在长元音如 /i:/, / :/, / :/, / :/, /u:/, / :/, /u:/, / :/ 中可以看到。反之,/ :/ 中可以看到。反之,/ /, /e/, / /, /e/, / /, / /, / /, / /, / /, / /, /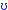 /, / /, / / 就称为短元音。由两个不同的符号组成的元称为双元音,如 /e / 就称为短元音。由两个不同的符号组成的元称为双元音,如 /e /, /a /, /a /, / /, /  /, / /, / 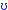 /, /a /, /a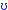 /, / /, /  /, /e /, /e / 和 / / 和 /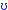  /。双元音由元音开头,滑音结尾;发双元音时,会由一个音的位置移动到另一个位置。 /。双元音由元音开头,滑音结尾;发双元音时,会由一个音的位置移动到另一个位置。
5. (r)如何发音
在诸如 far /f :(r)/ 等单词中,符号(r)在英式发音中,只有在下一个字的第一个音是元音时 /r/ 才发音,例如 far away /f :(r)/ 等单词中,符号(r)在英式发音中,只有在下一个字的第一个音是元音时 /r/ 才发音,例如 far away /f :(r) :(r)  we we /,否则 (r) 都不发音。而在美式英语里,所有的 /r/ 音都应该发出来。 /,否则 (r) 都不发音。而在美式英语里,所有的 /r/ 音都应该发出来。
6. 成音节辅音 /l/ 和 /n/
通常一个音节包含一个元音。然而,/l/ 和 /n/ 有时不需要元音,也能自成一个音节,如bottle / b b tl/ 和 button / tl/ 和 button / b b tn/。 tn/。
7. 弱元音 /i/ 和 /u/
必须清楚区分 /i:/ 和 / / 所代表的读音,可比较 heat /hi:/ 和 hit /h / 所代表的读音,可比较 heat /hi:/ 和 hit /h t/ 的差别。符号 /i/ 表示元音可以念 /i:/,也可以念 / t/ 的差别。符号 /i/ 表示元音可以念 /i:/,也可以念 / /,或表示该音介于 /i:/ 和 / /,或表示该音介于 /i:/ 和 / / 两者之音。有时年轻人喜欢把 /i/ 念成 /i:/,但音长较短,如 happy / / 两者之音。有时年轻人喜欢把 /i/ 念成 /i:/,但音长较短,如 happy / h h pi/。 pi/。
同时 /i:/ 与 / / 两个元音必须清楚区分,但 /u/ 则代表介于两者间的弱元音。如果 /u/ 之后紧接辅音,也可以发成 / / 两个元音必须清楚区分,但 /u/ 则代表介于两者间的弱元音。如果 /u/ 之后紧接辅音,也可以发成 / /。如 stimulate 也可以念成 / /。如 stimulate 也可以念成 / st st mjule mjule t/,也可以念成 / t/,也可以念成 / st st mj mj le le t/。 t/。
8. 主重音与次重音
含一个音节以上的单词一定都有重音 / /,如 butter / /,如 butter / b b t t / 和 calendar / / 和 calendar / k k l l nd nd /。比较长的词的重音之前可能含有次重音 / /。比较长的词的重音之前可能含有次重音 / /,例如 academic / /,例如 academic /  k k  dem dem k/ 和 independence / k/ 和 independence /  nd nd  pend pend ns/。 ns/。 |

